A circuit breaker is an electrical safety device designed to protect an electrical circuit from damage caused by current in excess of that which the equipment can safely carry (overcurrent). Its basic function is to interrupt current flow to protect equipment and to prevent fire. Unlike a fuse, which operates once and then must be replaced, a circuit breaker can be reset (either manually or automatically) to resume normal operation.
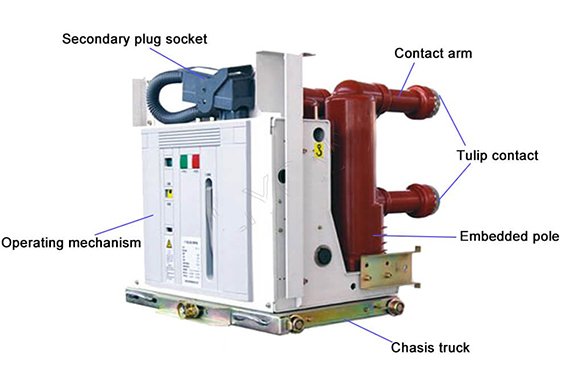

Vacuum Circuit Breakers (VCBs) are advanced devices used to protect electrical circuits from overloads and short circuits. They operate within a vacuum and offer high reliability and performance in various applications. Here are detailed aspects of VCBs:
Key Features:
- Fast Operating Speed: VCBs can interrupt faults very quickly, providing high-speed protection.
- Maintenance-Free: Because the contacts are in a vacuum, VCBs require minimal maintenance compared to other types of circuit breakers.
- Compact Design: VCBs are generally more compact than other circuit breakers with similar ratings.
- High Insulating Strength: The vacuum provides superior insulating properties, reducing the risk of dielectric failure.
Applications:
- Industrial Plants: Used in factories and plants to protect machinery and electrical systems.
- Commercial Buildings: Employed in high-rise buildings and large commercial spaces.
- Power Distribution: Suitable for utility and high voltage substations where reliability and performance are critical.





